Database Configuration
In CodeIgniter, go to application/config/databse.php for database configuration file.

In database.php file, fill the entries to connect CodeIgniter folder to your database.

The config settings are stored in a multi-dimensional array as shown above. Fill out your connection details to connect to database.
You can also specify failover in the situation where main connection cannot be established. This can be specified by setting failover as shown below. You can write as many failovers as you want.

Automatically connecting Database
The auto connect feature will load your database class with every page load.
To add auto connect go to application/config/autoload.php and add the word database to library array.
Manually connecting Database
If you need to connect database only in some pages of your project, you can use below code to add the database connectivity in any page, or add it to your class constructor which will make the database globally available for that class.
Connecting multiple Database
If you need to connect more than one database simultaneously, do the following.
- $db1 = $this->load->database(?group_one?, TRUE);
- $db1 = $this->load->database(?group_two?, TRUE);
Here, group_one and group_two are the group names which will be replaced by your group name
CodeIgniter Database INSERT record
In this example, we will INSERT different values in database showing meaning of Indian names through CodeIgniter.
In application/controller, file baby_form.php is created.
- <?php
- defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed');
-
- class Baby_form extends CI_Controller {
-
- public function index()
- {
- $this->load->view("baby_form_add");
- }
- function savingdata()
- {
-
- $data = array(
- 'name' => $this->input->post('name'),
- 'meaning' => $this->input->post('meaning'),
- 'gender' => $this->input->post('gender'),
- 'religion' => $this->input->post('religion')
- );
-
- $this->db->insert('baby',$data);
-
- redirect("baby_form/index");
- }
- }
- ?>
Look at the above snapshot, our table name is 'baby'.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Baby Form Add</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <form method="post" action="<?php echo site_url('baby_form/savingdata'); ?>">
- <table>
- <tr>
- <td>Name:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="name"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Meaning:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="meaning"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Gender:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="gender"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Religion:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="religion"></td>
- </tr><br><br>
- <tr>
- <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Save">
- </tr>
- </table>
- </form>
- </body>
- </html>
This is our view page which is being loaded in the controller's page.
To run it on your browser, pass URL
http://localhost/insert/index.php/Baby_form/
By inserting various names in the above form we have created our table as shown below.
CodeIgniter SELECT Database record
To fetch all data from database, one more page in Model folder of CodeIgniter will be created. There will be some changes in controller's and view's files also.
Controller file (Baby_form.php) is shown below.
- <?php
- defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed');
-
- class Baby_form extends CI_Controller {
-
- public function __construct()
- {
- parent::__construct();
-
-
- $this->load->model("Babymodel", "a");
- }
-
- public function index()
- {
- $this->load->view("baby_form_select");
- }
- function savingdata()
- {
-
- $data = array(
- 'name' => $this->input->post('name'),
- 'meaning' => $this->input->post('meaning'),
- 'gender' => $this->input->post('gender'),
- 'religion' => $this->input->post('religion')
- );
-
- $this->db->insert('baby',$data);
-
- redirect("baby_form/index");
- }
- }
- ?>
We have added a constructor to load the model page. Highlighted code is added to fetch the inserted record. And our view page is now baby_form_select.php
View file (baby_form_select.php) is shown below.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Baby Form Add</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <form method="post" action="<?php echo site_url('baby_form/savingdata'); ?>">
- <table>
- <tr>
- <td>Name:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="name"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Meaning:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="meaning"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Gender:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="gender"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td>Religion:</td>
- <td>:</td>
- <td><input type="text" name="religion"></td>
- </tr><br><br>
- <tr>
- <input type="submit" name="submit" value="Save">
- </tr>
- </table>
- </form>
- <table border="1">
- <thead>
- <th>ID</th>
- <th>NAME</th>
- <th>MEANING</th>
- <th>GENDER</th>
- <th>RELIGION</th>
- <th>ACTION</th>
- </thead>
- <tbody>
- <?php
- foreach($this->a->fetchtable() as $row)
- {
-
- echo "<tr>
- <td>$row->id</td>
- <td>$row->name</td>
- <td>$row->meaning</td>
- <td>$row->gender</td>
- <td>$row->religion</td>
- </tr>";
- }
- ?>
- </tbody>
- </table>
- </body>
- </html>
Code in baby_form_select.php file is same as baby_form_add.php. Above codes are added to fetch the record.
Here we have fetched the record in a table with the help of foreach loop. Function fetchtable() is created to fetch the record.
Model file (babymodel.php) is shown below.
- <?php
- defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed');
-
- class Babymodel extends CI_Model {
-
- function __construct()
- {
-
- parent::__construct();
- }
-
- function fetchtable()
- {
- $query = $this->db->get('baby');
- return $query->result();
- }
- }
- ?>
In URL, type http://localhost/CodeIgniter/index.php/Baby_form
Look at the above snapshot, all data has been fetched from the table 'baby'.
Login Form in CodeIgniter (without MySQL)
Here, we'll make a simple login page with the help of session.
Go to file autoload.php in application/config/autoload.php
Set session in library and helper.
Create controller page Login.php in application/controllers folder.
- <?php
- defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed');
-
- class Login extends CI_Controller {
-
- public function index()
- {
- $this->load->view('login_view');
- }
- public function process()
- {
- $user = $this->input->post('user');
- $pass = $this->input->post('pass');
- if ($user=='juhi' && $pass=='123')
- {
-
- $this->session->set_userdata(array('user'=>$user));
- $this->load->view('welcome_view');
- }
- else{
- $data['error'] = 'Your Account is Invalid';
- $this->load->view('login_view', $data);
- }
- }
- public function logout()
- {
-
- $this->session->unset_userdata('user');
- redirect("Login");
- }
-
- }
- ?>
Look at the above snapshot, we have created a session for a single user with Username juhi and Password 123. For a valid login and logout we will use this username and password.
Create view page login_view.php in application/views folder.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Login Page</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <?php echo isset($error) ? $error : ''; ?>
- <form method="post" action="<?php echo site_url('Login/process'); ?>">
- <table cellpadding="2" cellspacing="2">
- <tr>
- <td><th>Username:</th></td>
- <td><input type="text" name="user"></td>
- </tr>
- <tr>
- <td><th>Password:</th></td>
- <td><input type="password" name="pass"></td>
- </tr>
-
- <tr>
- <td> </td>
- <td><input type="submit" value="Login"></td>
- </tr>
- </table>
- </form>
- </body>
- </html>
Create view page welcome_view.php in application/views folder to show the successful login message.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title></title>
- </head>
- <body>
- Welcome <?php echo $this->session->userdata('user'); ?>
- <br>
- <?php echo anchor('Login/logout', 'Logout'); ?>
-
-
- </body>
- </html>
Output
Type URL localhost/login/index.php/Login
Now on entering wrong information we'll be see unsuccessful message which we have set in login_view page in else part.
Now on entering right information, we'll see welvome_view.php message.
Click on Logout, we'll be directed to Login page.
Login page (with database)
In earlier example, we learnt a simple login page with one single username and session.
Now we'll make it with more than one users using database. A sign in and login page will be there for users.
Following pages are made in this example.
In application/controllers
In application/views
- login_view.php
- invalid.php
- data.php
- signin.php
In application/models
In the first page, you'll have the option for Login and Sign In.
On Login, if user has entered correct credentials matching to database then he will be directed to data.php page. But if he has entered wrong information then incorrect username/password message will appear.
We have named our CodeIgniter folder as login_db. And our table name is signup.
We need to do some basic settings in our login_db CodeIgniter folder.
Go to autoload.php file, and do the following settings.
In the above snpashot, we have loaded the libraries and helper.
In database.php file, fill your username and database name. Our database name is codeigniter.
Now, we?ll start the example.
We have made file Main.php in application/controllers folder,
- <?php
- defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed');
-
- class Main extends CI_Controller {
-
- public function index()
- {
- $this->login();
- }
-
- public function login()
- {
- $this->load->view('login_view');
- }
-
- public function signin()
- {
- $this->load->view('signin');
- }
-
- public function data()
- {
- if ($this->session->userdata('currently_logged_in'))
- {
- $this->load->view('data');
- } else {
- redirect('Main/invalid');
- }
- }
-
- public function invalid()
- {
- $this->load->view('invalid');
- }
-
- public function login_action()
- {
- $this->load->helper('security');
- $this->load->library('form_validation');
-
- $this->form_validation->set_rules('username', 'Username:', 'required|trim|xss_clean|callback_validation');
- $this->form_validation->set_rules('password', 'Password:', 'required|trim');
-
- if ($this->form_validation->run())
- {
- $data = array(
- 'username' => $this->input->post('username'),
- 'currently_logged_in' => 1
- );
- $this->session->set_userdata($data);
- redirect('Main/data');
- }
- else {
- $this->load->view('login_view');
- }
- }
-
- public function signin_validation()
- {
- $this->load->library('form_validation');
-
- $this->form_validation->set_rules('username', 'Username', 'trim|xss_clean|is_unique[signup.username]');
-
- $this->form_validation->set_rules('password', 'Password', 'required|trim');
-
- $this->form_validation->set_rules('cpassword', 'Confirm Password', 'required|trim|matches[password]');
-
- $this->form_validation->set_message('is_unique', 'username already exists');
-
- if ($this->form_validation->run())
- {
- echo "Welcome, you are logged in.";
- }
- else {
-
- $this->load->view('signin');
- }
- }
-
- public function validation()
- {
- $this->load->model('login_model');
-
- if ($this->login_model->log_in_correctly())
- {
-
- return true;
- } else {
- $this->form_validation->set_message('validation', 'Incorrect username/password.');
- return false;
- }
- }
-
- public function logout()
- {
- $this->session->sess_destroy();
- redirect('Main/login');
- }
-
- }
- ?>
In application/views folder, login_view.php file is made.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html lang="en">
- <head>
- <meta charset="utf-8">
- <title>Login Page</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Login</h1>
-
- <?php
-
- echo form_open('Main/login_action');
-
- echo validation_errors();
-
- echo "<p>Username: ";
- echo form_input('username', $this->input->post('username'));
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo "<p>Password: ";
- echo form_password('password');
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo "</p>";
- echo form_submit('login_submit', 'Login');
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo form_close();
-
- ?>
-
- <a href='<?php echo base_url()."index.php/Main/signin"; ?>'>Sign In</a>
- </body>
- </html>
In application/views folder, data.php file is made.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title></title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Welcome, You are successfully logged in.</h1>
-
- <?php
- echo "<pre>";
- echo print_r($this->session->all_userdata());
- echo "</pre>";
- ?>
-
- <a href='<?php echo base_url()."index.php/Main/logout"; ?>'>Logout</a>
-
- </body>
- </html>
In application/views folder, signin.php file is made.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Sign Up Page</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Sign In</h1>
-
- <?php
-
- echo form_open('Main/signin_validation');
-
- echo validation_errors();
-
- echo "<p>Username:";
- echo form_input('email');
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo "<p>Password:";
- echo form_password('password');
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo "<p>Confirm Password:";
- echo form_password('cpassword');
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo "<p>";
- echo form_submit('signin_submit', 'Sign In');
- echo "</p>";
-
- echo form_close();
-
- ?>
-
- </body>
- </html>
In application/views folder, invalid.php file is made.
- <!DOCTYPE html>
- <html>
- <head>
- <title>Invalid Page</title>
- </head>
- <body>
- <h1>Sorry, You don't have access to this page.</h1>
-
- <a href='<?php echo base_url()."Main/login"; ?>'>Login Again</a>
-
- </body>
- </html>
In application/models folder, login_model.php file is made.
- <?php
-
- class Login_model extends CI_Model {
-
- public function log_in_correctly() {
-
- $this->db->where('username', $this->input->post('username'));
- $this->db->where('password', $this->input->post('password'));
- $query = $this->db->get('signup');
-
- if ($query->num_rows() == 1)
- {
- return true;
- } else {
- return false;
- }
-
- }
-
-
- }
- ?>
On entering the URL, http://localhost/login_db/index.php/Main/
Following page will appear.
Enter the information to Login.
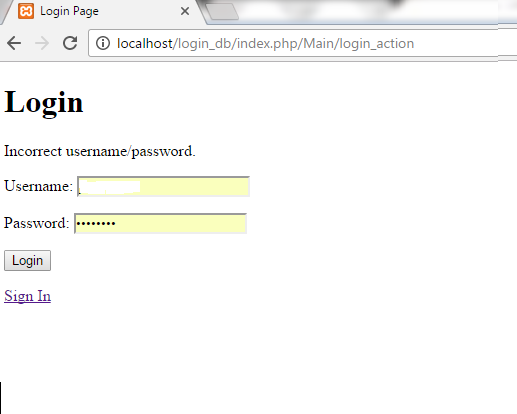
After entering information, click on
Login button. We have entered the wrong information and hence it will show the error message as shown below.
On entering the information from database, we' ll be directed to data.php page.
Click on Login button.
Clicking on Logout button, you'll be directed to the Main page.
On clicking Sign In, following page will appear.